Why LangGraph Is the Undisputed King of AI Agents in 2025
LangGraph provides the reliability, controllability, and scalability required for production systems while maintaining the flexibility needed for innovation.
Why LangGraph Is the Undisputed King of AI Agents in 2025
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, where autonomous agents are transforming how businesses operate and developers build applications, one framework has emerged as the clear leader: LangGraph. As we navigate through 2025, LangGraph has established itself as the undisputed king of AI agent frameworks, powering production systems at companies ranging from Uber and Replit to Klarna and LinkedIn. This comprehensive analysis explores the architectural innovations, production-ready capabilities, and ecosystem advantages that have cemented LangGraph's dominance in the AI agent space.
The Evolution of AI Agent Development
The journey to LangGraph's supremacy began with a fundamental recognition: building reliable AI agents requires more than just chaining together large language model (LLM) calls. Traditional approaches struggled with state management, complex workflows, error handling, and the unpredictable nature of LLM outputs. While LangChain provided the foundational tools for LLM integration, developers needed something more sophisticated for production-grade agent systems that could handle branching logic, cycles, human-in-the-loop interventions, and long-running stateful workflows.
LangGraph was built from the ground up to address these challenges. Unlike its predecessors and competitors, LangGraph treats agent workflows as directed graphs where each node represents a discrete computation (LLM calls, tools, functions) and edges define the flow of information and control. This graph-based architecture provides developers with unprecedented control over agent behavior while maintaining the flexibility required for complex, real-world applications.
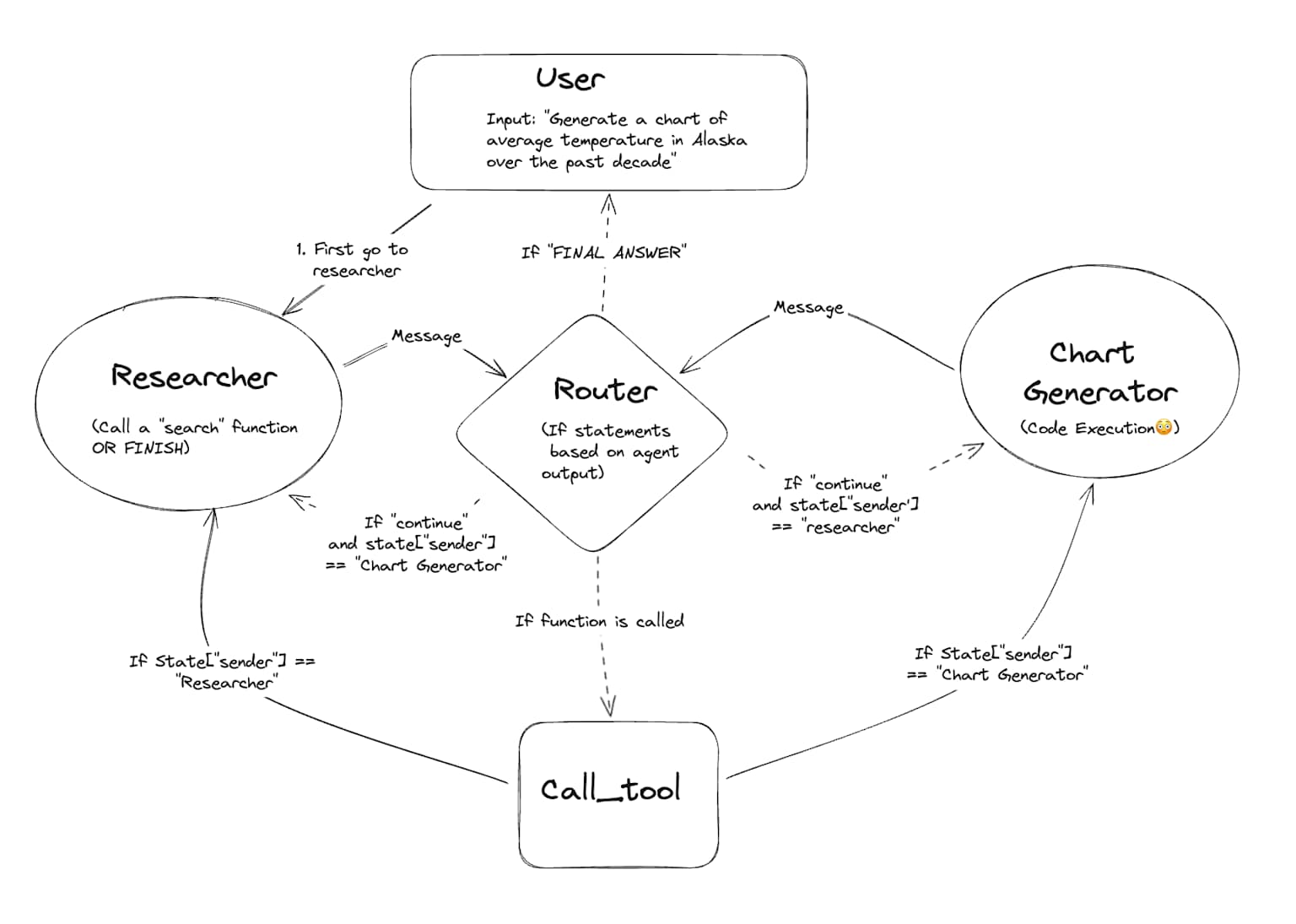
LangGraph: Multi-Agent Workflows
Graph-Based Architecture: The Foundation of Superiority
At the heart of LangGraph's dominance lies its graph-based orchestration model. Rather than forcing developers into linear chains or rigid conversational patterns, LangGraph allows the construction of sophisticated workflows as state machines with nodes and edges. This architectural decision provides several critical advantages that competing frameworks simply cannot match.
Explicit Control Flow and Branching Logic
LangGraph's graph structure enables developers to define conditional transitions between nodes based on the current state of the application. This means agents can make dynamic decisions about which operations to execute next, creating truly adaptive systems. For instance, a customer support agent can route conversations differently based on sentiment analysis, urgency detection, or topic classification—all represented as clear, visualizable graph transitions.
Unlike frameworks like CrewAI, which are limited to directed acyclic graphs (DAGs), LangGraph supports cyclic workflows. This capability is essential for iterative processes such as research agents that refine their queries based on search results, code generation systems that test and debug iteratively, or conversational agents that loop back for clarification. The ability to create cycles without getting trapped in infinite loops represents a sophisticated level of control that developers desperately need for production systems.
State Management as a First-Class Citizen
Perhaps no feature distinguishes LangGraph more clearly than its approach to state management. LangGraph treats state as a first-class citizen, providing automatic state persistence through its checkpointing system. Every node in a LangGraph workflow can read from and write to a shared state object, which is automatically saved at each "super-step" of execution.
This built-in persistence layer enables several powerful capabilities. First, it provides long-term memory across multiple interactions, allowing agents to maintain context over time without developers implementing custom storage solutions. Second, it supports fault tolerance by allowing workflows to resume from the last successful checkpoint after failures. Third, it enables time travel debugging, where developers can inspect the state at any point in execution history and even fork from previous checkpoints to test alternative paths.
The state management system extends beyond single conversations through LangGraph's memory store, which enables information sharing across different threads and sessions. This cross-thread memory capability allows agents to build user profiles, remember preferences, and apply learnings from one conversation to another—functionality that is essential for personalized, enterprise-grade applications.
Production-Ready Infrastructure: Where Competitors Fall Short
While many frameworks excel at prototyping and demonstrations, LangGraph stands alone in its production readiness. This distinction is not merely academic—it represents the difference between research projects and systems that power critical business operations at scale.
Human-in-the-Loop: Trust Through Control
One of LangGraph's most celebrated features is its comprehensive support for human-in-the-loop (HITL) workflows. In production environments, fully autonomous agents are often inappropriate or even dangerous for sensitive operations. LangGraph was designed from day one to support human intervention at any point in a workflow through its interrupt system.
LangGraph provides two mechanisms for implementing HITL: dynamic interrupts and static interrupts. Dynamic interrupts allow agents to pause execution from within a node based on runtime conditions, effectively asking for human assistance when needed. Static interrupts enable developers to define specific points in the graph where execution should pause for approval—perfect for scenarios like approving API calls, reviewing generated content, or validating critical decisions.
What makes LangGraph's HITL implementation superior is its persistent execution state. Because LangGraph checkpoints the graph state at each step, workflows can pause indefinitely while waiting for human input and resume exactly where they left off—even if the server restarts or hours pass between the pause and resumption. This asynchronous capability is impossible to achieve cleanly in frameworks without built-in persistence.
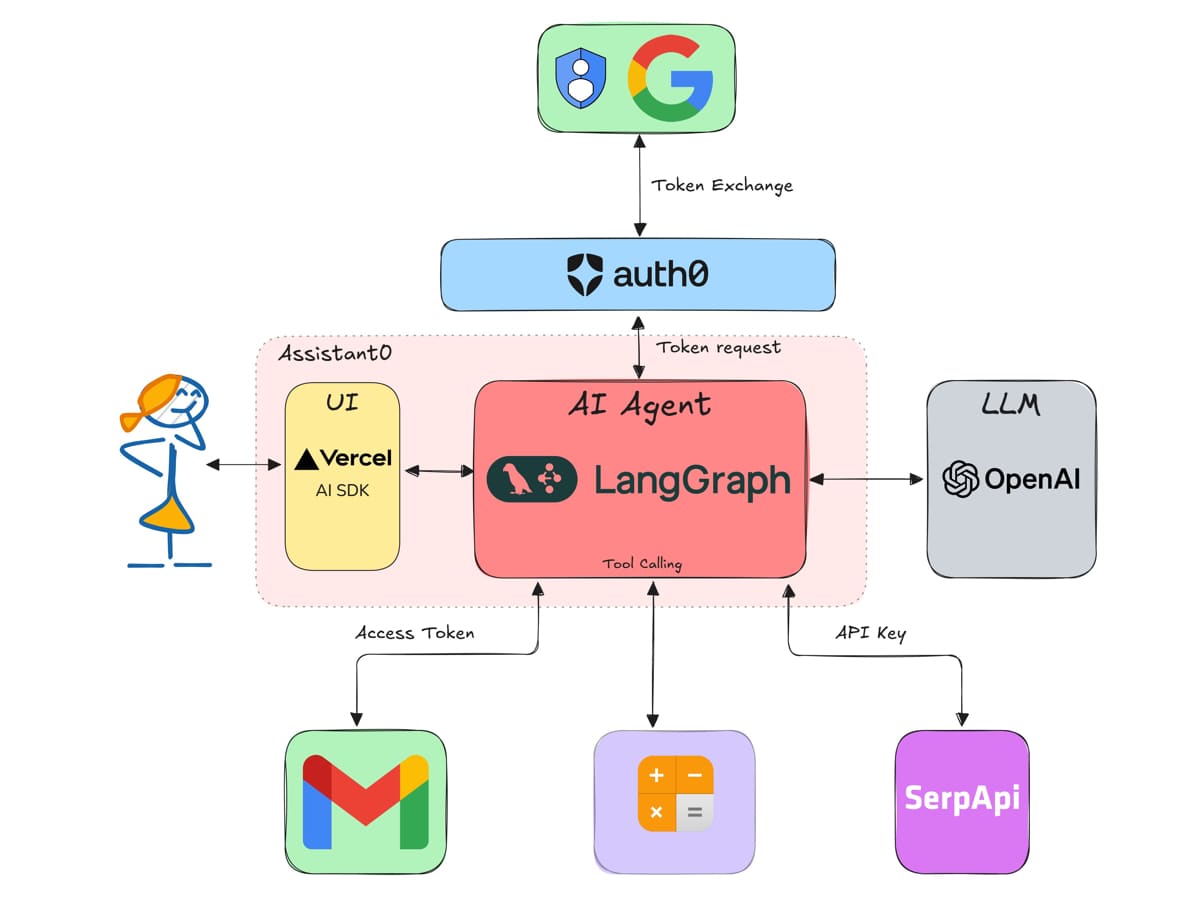
How to build an AI Assistant with LangGraph and Next.js
Streaming for Real-Time Responsiveness
Modern AI applications demand real-time feedback to keep users engaged. LangGraph delivers industry-leading streaming capabilities through multiple modalities. The framework supports streaming at three distinct levels: workflow progress (state updates after each node execution), LLM token streaming (word-by-word generation), and custom update events (application-specific notifications).
LangGraph's .stream() and .astream() methods provide flexible streaming modes including "values" (complete state), "updates" (incremental changes), "messages" (message-specific streaming), and "debug" (detailed execution information). This granular control allows developers to create responsive user experiences tailored to their specific application needs, whether showing agent reasoning steps in real-time or displaying LLM outputs as they generate.
The framework's streaming system is particularly powerful for complex workflows because it can stream from nested subgraphs and capture token streams from any point in the execution tree. This means even deeply nested agent operations remain visible to end users, maintaining transparency and engagement throughout long-running processes.
Enterprise Deployment and Scalability
LangGraph's production infrastructure extends far beyond the framework itself through LangSmith Deployment (formerly LangGraph Platform). This deployment layer provides the operational capabilities that enterprises demand: one-click deployment, horizontal scaling for bursty traffic, comprehensive API endpoints for custom user experiences, and a purpose-built persistence layer for stateful, long-running workflows.
The platform offers multiple deployment options tailored to different enterprise requirements. Organizations can choose from Cloud SaaS (fully managed), Self-Hosted Data Plane (hybrid control), Self-Hosted Control Plane (complete ownership), or Standalone Container (maximum flexibility). This flexibility allows companies to balance convenience with security and compliance requirements—a critical consideration for regulated industries like finance and healthcare.
Real-world performance validates LangGraph's scalability claims. Companies like Klarna, with 85 million active users, rely on LangGraph to power their AI-driven customer support systems. Uber uses LangGraph to orchestrate large-scale code migrations and unit test generation across their developer platform. These deployments demonstrate that LangGraph can handle production workloads at genuine enterprise scale.
Developer Experience: The Competitive Moat
Beyond technical capabilities, LangGraph has built a substantial competitive advantage through superior developer experience. This advantage manifests across documentation, tooling, community support, and ecosystem integration—factors that determine whether frameworks achieve widespread adoption or remain niche solutions.
Visualization and Debugging Tools
LangGraph provides LangSmith Studio, a specialized IDE for visualizing, interacting with, and debugging agent workflows. Studio displays graph architecture as an interactive diagram, allows developers to run agents step-by-step while inspecting state changes, enables time-travel debugging by rewinding to any checkpoint, and provides detailed tracing of every node execution.
The visualization capabilities serve multiple purposes beyond debugging. They facilitate team collaboration by providing a shared understanding of complex agent logic. They enable stakeholder communication by making AI behavior transparent to non-technical decision-makers. They accelerate onboarding by helping new team members quickly grasp existing agent architectures.
Developers report that Studio's ability to set breakpoints and rerun specific nodes dramatically accelerates the development cycle. Instead of running entire workflows to test a single change, developers can execute a graph up to a specific node, modify code, and rerun just that portion—a workflow that mirrors traditional software debugging but adapted for agent systems.
Comprehensive Ecosystem Integration
LangGraph benefits from its position within the LangChain ecosystem, inheriting access to a vast array of integrations, tools, and community resources. With over 80,000 GitHub stars and adoption by hundreds of companies, the ecosystem provides pre-built connectors for virtually every LLM provider, vector database, tool, and API that developers might need.
This ecosystem advantage creates powerful network effects. When developers choose LangGraph, they gain immediate access to solutions for common problems: RAG implementations, memory systems, prompt templates, evaluation frameworks, and monitoring tools. The comprehensive documentation includes not just API references but architectural patterns, best practices, and real-world case studies.
The ecosystem extends to complementary tools. LangSmith provides observability with detailed tracing, performance metrics, and cost analytics for debugging and optimizing production agents. LangServe enables rapid API deployment for LangGraph applications. Langflow and Flowise offer visual, low-code interfaces for building LangGraph workflows. This tooling maturity is unmatched by newer frameworks still building their foundational capabilities.
Maintainability and Code Quality
LangGraph's architecture promotes maintainable, readable code. The graph structure serves as living documentation—developers can understand an agent's logic by examining its node definitions and edge conditions without tracing through complex callback chains or implicit state management.
The framework's functional design patterns encourage clean separation of concerns. Each node is a discrete function with clear inputs (state) and outputs (state updates), making unit testing straightforward. The explicit state schema prevents bugs caused by unexpected state mutations that plague less structured approaches.
AI researchers and developers interviewed about their LangGraph experiences consistently highlight how the framework helps them abstract flow logic and avoid boilerplate code. One AI researcher at Nokia explained: "LangGraph helped abstract the flow logic and avoid having to write all of the boilerplate code to get started with the project". This productivity gain is especially valuable for teams building multiple agents or iterating rapidly on agent designs.
Competitive Landscape: Why Alternatives Fall Short
To fully appreciate LangGraph's dominance, it's instructive to examine where competing frameworks fall short. The AI agent landscape in 2025 includes several notable alternatives—AutoGen, CrewAI, OpenAI Swarm, and Semantic Kernel—each with specific strengths but fundamental limitations that prevent them from matching LangGraph's comprehensive capabilities.
AutoGen: Simplicity vs. Complexity
Microsoft's AutoGen excels at building conversational multi-agent systems through its dialogue-based approach. Its AutoGen Studio provides a visual interface that accelerates prototyping, and its minimal coding requirements enable rapid deployment for straightforward conversational workflows.
However, AutoGen's conversational paradigm becomes a liability for complex, non-conversational workflows. The framework lacks LangGraph's sophisticated state management, making it difficult to handle workflows with intricate branching logic or long-term context requirements. AutoGen's visualization tools, while user-friendly for simple cases, cannot match Studio's depth for debugging complex agent interactions.
Performance comparisons reveal AutoGen's limitations. While AutoGen handles thousands of concurrent conversations efficiently for chat-based applications, it struggles with the iterative, stateful workflows that LangGraph handles naturally. Developers building production systems consistently report choosing LangGraph over AutoGen when their requirements extend beyond basic conversational patterns.
CrewAI: Role-Based Simplicity
CrewAI differentiates itself through role-based agent orchestration, where agents have defined roles and collaborate to accomplish tasks. This approach is intuitive for scenarios that map naturally to human team structures, such as content creation pipelines with writer, editor, and fact-checker agents.
CrewAI's fundamental limitation is its restriction to directed acyclic graphs—it cannot handle cycles. This architectural constraint eliminates entire categories of applications that require iterative refinement, such as research agents that progressively deepen their investigation or code generators that test and fix bugs iteratively. A developer directly compared the frameworks: "CrewAI can only handle DAGs and cannot handle cycles, whereas LangGraph can handle complex graph flows, including cycles".
Additionally, CrewAI's abstractions, while initially helpful, become constraining as requirements grow more sophisticated. LangGraph's lower-level primitives provide the flexibility to implement any pattern, including role-based collaboration when appropriate, without being locked into a specific paradigm.
OpenAI Swarm: Experimental Limitations
OpenAI Swarm, announced as a lightweight framework for multi-agent coordination, generated significant interest due to its official backing from OpenAI. However, Swarm explicitly remains experimental and is not recommended for production use. Its simplicity and ease of use make it attractive for learning and prototyping, but it lacks the production-ready features that enterprises require.
LangGraph provides superior control for complex workflows while maintaining production-grade reliability. The comparison is stark: Swarm is explicitly positioned as a learning tool, while LangGraph powers critical systems at Fortune 500 companies. Organizations seeking to move beyond experimentation consistently choose LangGraph for its comprehensive feature set and proven scalability.
Real-World Impact: Production Success Stories
The ultimate validation of LangGraph's superiority comes from its production deployments across diverse industries and use cases. These implementations demonstrate not just technical capability but business value—agents that deliver measurable improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and user satisfaction.
Enterprise Adoption Across Industries
LinkedIn, one of the world's largest professional networks, uses LangGraph to power search and code generation capabilities. Meta leverages LangGraph for code generation and search discovery, with multiple blog posts detailing their production experiences. J.P. Morgan and BlackRock, titans of the financial services industry, have adopted LangGraph for domain-specific copilots that assist with complex financial analysis.
The healthcare sector has embraced LangGraph for applications where reliability is literally life-critical. City of Hope and Komodo Health use LangGraph to build copilots for medical professionals, while OpenRecovery developed patient care agents powered by the framework. These deployments underscore LangGraph's ability to meet the stringent reliability and compliance requirements of regulated industries.
Replit, the browser-based development environment, built their groundbreaking Replit Agent on LangGraph. This agent serves as a copilot for building complete software applications from scratch, showcasing LangGraph's capabilities for multi-step reasoning, tool use, and human-in-the-loop collaboration. President Michele Catasta specifically highlighted the importance of LangGraph's HITL features in their fireside chat, noting how users need visibility into agent actions from package installations to file creation.
Measurable Business Outcomes
These deployments deliver quantifiable value. AppFolio created a copilot that saves over 10 hours per week for property managers while cutting application latency and doubling decision accuracy. Uber dramatically accelerated their code migration processes by using LangGraph to orchestrate specialized agents for unit test generation. Elastic improved their security posture by using LangGraph to coordinate AI agents for real-time threat detection, enabling faster response to security risks.
A comprehensive analysis found that organizations using LangGraph report 25-30% increases in developer productivity due to intuitive APIs and comprehensive documentation. Teams achieve 40% faster time-to-market through LangGraph's modular architecture enabling rapid prototyping and deployment. The framework's built-in error handling and retry mechanisms reduce production error rates by 35% compared to custom implementations.
Industry Survey Data
Survey data from 2025 reveals that 90% of respondents working in non-tech companies have or are planning to put agents into production, with many specifically choosing LangChain/LangGraph for its maturity and extensive ecosystem. Among developers working with AI agent frameworks, LangGraph leads adoption by a significant margin, with comprehensive community support cited as a primary decision factor.
The State of Agent Engineering report indicates that observability and evaluation are top priorities for teams building production agents. LangGraph's integration with LangSmith directly addresses these needs, providing the monitoring and testing infrastructure that organizations require to deploy agents confidently. This alignment between developer needs and framework capabilities explains LangGraph's continued growth in enterprise contexts.
Technical Deep Dive: Advanced Capabilities
Beyond the foundational features that establish LangGraph's leadership, the framework provides advanced capabilities that enable sophisticated applications. These features address the complex requirements of production systems while maintaining developer-friendly interfaces.
Multi-Agent Orchestration Patterns
LangGraph supports diverse multi-agent patterns including hierarchical structures, dynamic group chats, and parallel execution. Unlike frameworks that force specific collaboration models, LangGraph provides primitives for developers to implement any orchestration pattern their use case demands.
The framework enables explicit agent routing where a supervisor agent analyzes situations and delegates to specialized sub-agents. This pattern is powerful for customer support systems where a routing agent directs queries to product specialists, technical support, or billing departments based on the content and context. Each specialized agent can have its own state, tools, and workflows while communicating through the shared graph state.
For applications requiring parallel execution, LangGraph supports concurrent node execution where multiple agents process different aspects of a problem simultaneously and then converge their results. A research assistant might dispatch parallel agents to search academic databases, news sources, and technical documentation, then synthesize the findings in a coordinating node. This parallelization dramatically reduces latency for information-intensive workflows.
Memory and Context Management
LangGraph's memory system operates at multiple levels to support different use cases. Short-term memory, implemented through thread-scoped checkpointers, maintains conversation history within a session. This enables multi-turn dialogues where the agent remembers what the user said earlier in the conversation.
Long-term memory, enabled by the memory store, persists information across sessions and threads. A customer service agent can remember a user's preferences, purchase history, and past issues across multiple interactions spanning days or weeks. The MongoDB Store integration for LangGraph, announced in 2025, provides production-ready cross-thread memory with automatic TTL indexes for managing memory lifecycle.
Developers can implement hybrid memory strategies combining short-term and long-term memory. An agent might maintain detailed conversation context in short-term memory while extracting key facts to long-term memory for future reference. This flexibility allows optimization for both context richness and performance, as long-term memory queries can be selectively triggered rather than loading all historical data for every interaction.
Error Handling and Reliability
Production systems must gracefully handle failures, and LangGraph provides comprehensive error handling capabilities. The framework supports retry logic at the node level, allowing developers to specify retry policies for operations that might fail transiently (API timeouts, rate limits, temporary service unavailability).
The checkpointing system itself provides fault tolerance. If a workflow fails mid-execution, LangGraph stores pending writes from successfully completed nodes, ensuring that when execution resumes, the workflow doesn't re-run operations unnecessarily. This is critical for expensive operations like large API calls or complex computations that shouldn't be repeated after partial failure.
LangGraph enables graceful degradation through conditional routing based on error states. An agent can be designed to fall back to simpler strategies when sophisticated approaches fail, ensuring the user receives some response even when optimal behavior is unavailable. This resilience is essential for maintaining user trust in production applications where perfection is impossible but consistent reliability is mandatory.
The Ecosystem Advantage: Network Effects in Action
LangGraph's position within the broader LangChain ecosystem creates powerful network effects that compound its technical advantages. As more developers adopt LangGraph, the ecosystem generates more tools, integrations, examples, and community knowledge—which in turn attracts more developers in a self-reinforcing cycle.
Community and Documentation
The LangGraph community, part of the larger LangChain ecosystem with 80,000+ GitHub stars, represents one of the largest and most active AI developer communities. This community generates continuous contributions: tutorials, blog posts, GitHub repositories, Stack Overflow answers, and Discord conversations that collectively form an invaluable knowledge base.
The official documentation sets industry standards for comprehensiveness. It includes not just API references but conceptual guides, architectural patterns, how-to tutorials, real-world case studies, and migration guides. Developers consistently report that LangGraph's documentation quality significantly reduces learning curves compared to competing frameworks.
Community-created resources extend the official documentation. The awesome-LangGraph repository curates projects, tools, and learning resources. Numerous YouTube channels provide video tutorials covering everything from basic concepts to advanced patterns. This wealth of learning materials ensures developers can find answers regardless of their experience level or learning style.
Third-Party Integrations and Tools
The ecosystem includes extensive third-party integrations that extend LangGraph's capabilities. Vector database providers like Pinecone, Weaviate, and Chroma offer native LangGraph integrations. Observability platforms like Langfuse provide specialized monitoring for LangGraph applications. Database solutions including PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and SQLite have official checkpointer and store implementations.
Tool providers actively ensure LangGraph compatibility. Arcade, which provides secure tool execution for AI agents, specifically highlights LangGraph integration, noting that 87% of IT executives rate interoperability as crucial for agentic AI adoption. This ecosystem alignment means developers can confidently adopt LangGraph knowing that their tool choices will integrate smoothly.
Corporate Backing and Roadmap
LangGraph benefits from the corporate backing of LangChain Inc., which provides commercial support, professional services, and continuous development. The company's commitment to open-source development while offering commercial deployment options creates a sustainable model that reassures enterprises investing in the technology.
The product roadmap demonstrates responsiveness to enterprise needs. Recent additions include enhanced memory management, improved debugging tools, expanded deployment options, and performance optimizations—all driven by feedback from production users. This iterative improvement process, informed by real-world usage at scale, ensures LangGraph continues evolving to meet emerging requirements.
Looking Forward: LangGraph's Sustainable Leadership
As we assess the AI agent landscape in 2025, several factors suggest LangGraph's dominance will not only persist but strengthen. The framework's architectural foundation is sound, its production track record is proven, its ecosystem is mature, and its development velocity remains high.
Emerging Trends and LangGraph's Position
The shift toward agentic workflows in enterprise AI represents a fundamental transformation from traditional chatbots to autonomous systems that can reason, plan, and act. LangGraph is uniquely positioned for this shift, as its graph-based architecture naturally expresses complex agent behaviors that simpler frameworks cannot represent.
The increasing importance of observability and evaluation in production AI systems plays to LangGraph's strengths. The integration with LangSmith provides the monitoring and debugging capabilities that teams need to confidently deploy agents in critical business processes. As AI governance and compliance requirements grow, this observability advantage will become even more valuable.
The proliferation of specialized AI models and the trend toward multi-model systems favors LangGraph's tool-agnostic design. Unlike frameworks tightly coupled to specific LLM providers, LangGraph abstracts model interactions, allowing developers to mix and match models based on task requirements. This flexibility will prove crucial as the model landscape continues fragmenting and specializing.
The Competition's Response
Competing frameworks are responding to LangGraph's success by adopting similar patterns. CrewAI has announced work on supporting cycles, AutoGen is developing better state management, and new frameworks explicitly cite LangGraph as inspiration. This imitation validates LangGraph's architectural choices while simultaneously making the framework's head start even more valuable.
However, matching LangGraph's capabilities requires more than adding features. The framework's advantage lies in its holistic design—the way state management, persistence, streaming, error handling, and human-in-the-loop capabilities work together seamlessly. Competitors face the challenge of retrofitting these capabilities into architectures designed without them, often resulting in awkward abstractions or breaking changes.
The ecosystem advantage proves particularly difficult to replicate. Years of community contributions, documentation, integrations, and production learnings cannot be quickly duplicated. Even well-funded competitors must invest years building comparable ecosystems, during which time LangGraph's network effects continue compounding.
Conclusion: The Verdict on LangGraph's Reign
LangGraph's position as the undisputed king of AI agents in 2025 rests on multiple pillars: superior graph-based architecture enabling complex, cyclic workflows; comprehensive state management with built-in persistence; production-ready infrastructure including HITL, streaming, and deployment options; exceptional developer experience through visualization and debugging tools; a mature ecosystem with extensive integrations and community support; and proven enterprise adoption delivering measurable business value.
The framework's success stories span industries and use cases, from Uber's code migrations to Klarna's customer support, from Replit's development agents to healthcare copilots. These deployments demonstrate that LangGraph delivers not just technical capability but genuine business impact through improved efficiency, accuracy, and user satisfaction.
For developers and organizations building AI agents in 2025, the choice is clear. LangGraph provides the reliability, controllability, and scalability required for production systems while maintaining the flexibility needed for innovation. Its architecture supports everything from simple chatbots to sophisticated multi-agent systems, its tooling accelerates development and debugging, and its ecosystem ensures long-term viability.
As the AI agent landscape continues evolving, LangGraph's architectural foundations, production track record, and ecosystem momentum position it not just as the current leader but as the framework shaping the future of autonomous AI systems. The question for 2025 and beyond is not whether LangGraph will maintain its dominance, but how competing frameworks will attempt to catch up with the undisputed king of AI agents.