Top 10 AI Agent Trends Shaping 2025: From Voice to Vision
The ten transformative trends explored in this analysis from voice and vision to memory, reasoning, collaboration, and security collectively define the agentic reshaping enterprise technology.
Top 10 AI Agent Trends Shaping 2025: From Voice to Vision
The landscape of artificial intelligence is undergoing a dramatic transformation in 2025, marked by the explosive rise of AI agents—autonomous systems that don't just respond to queries but reason, plan, and take action across complex workflows. This shift from generative AI to agentic AI represents one of the most significant inflections in enterprise technology, with 85% of enterprises now deploying AI agents and the market projected to reach $150 billion by year's end. These intelligent systems are revolutionizing industries from healthcare to finance, manufacturing to customer service, fundamentally changing how organizations operate and how humans interact with technology. This comprehensive analysis explores the ten most transformative AI agent trends of 2025, examining their technological underpinnings, real-world applications, and profound implications for the future of work.
The convergence of advanced capabilities—from voice and vision to memory and reasoning—is creating AI agents that function less like tools and more like autonomous digital teammates. With 97% of enterprises adopting voice AI technology and 52% already deploying agents in production environments, we're witnessing the dawn of what industry leaders call the "agentic era". These trends aren't merely incremental improvements; they represent a fundamental reimagining of how intelligent systems perceive their environments, process information, and execute tasks with unprecedented autonomy and sophistication.
The Rise of Voice AI Agents: Conversations at the Speed of Thought
Voice AI agents have reached a critical inflection point in 2025, evolving from rigid command-response systems into sophisticated conversational partners capable of natural, human-like interactions. The breakthrough that distinguishes modern voice agents from their predecessors lies in native audio understanding—systems that process speech directly without the latency-inducing pipeline of speech-to-text conversion, LLM processing, and text-to-speech synthesis. This architectural shift has reduced response latency to sub-100 milliseconds, creating conversations that feel genuinely natural and eliminating the awkward pauses that plagued earlier implementations.
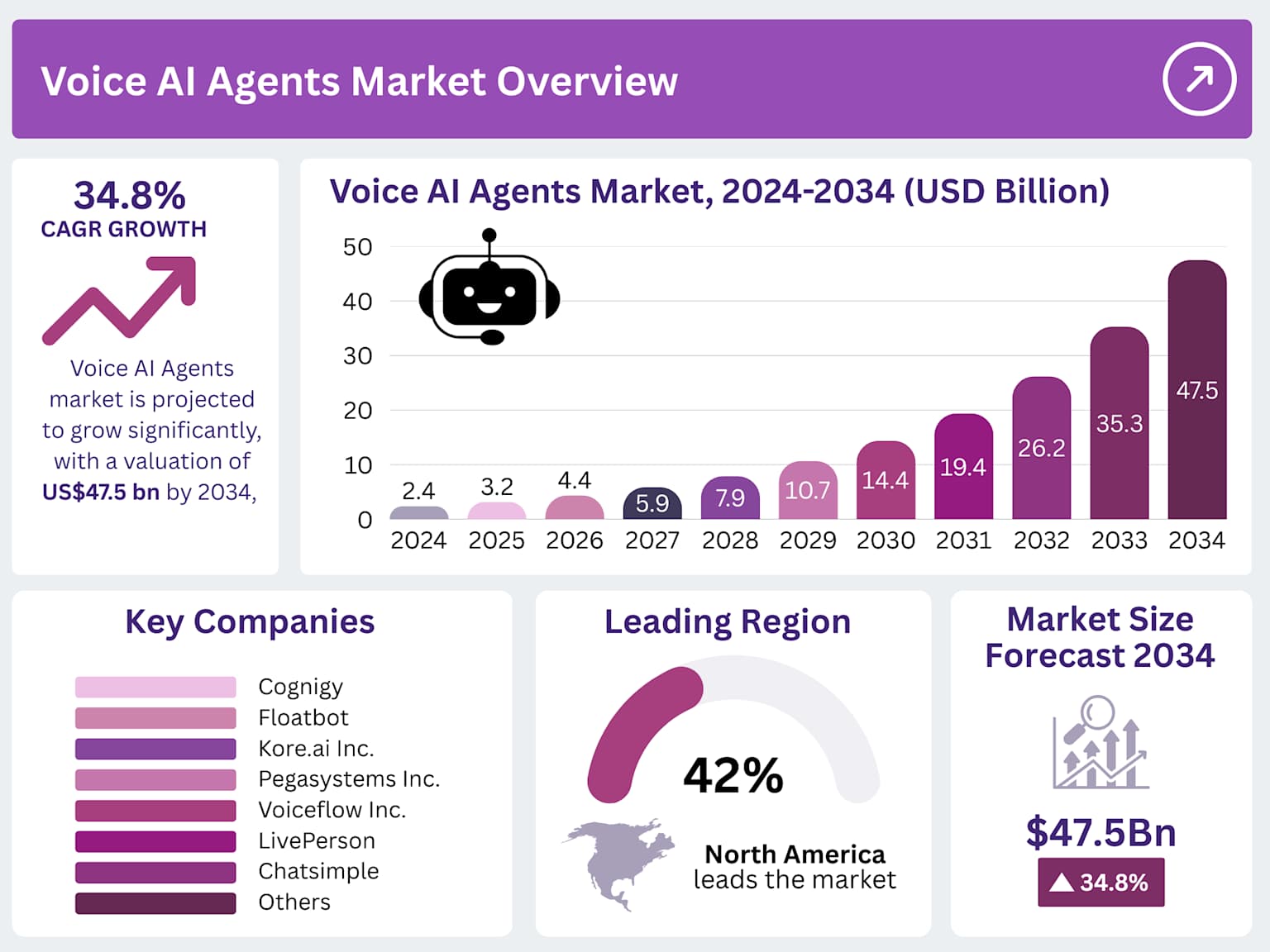
Voice AI Agents Market to hit USD 47.5 Bn By 2034
The technological foundation enabling this transformation combines several critical innovations. Advanced orchestrated speech systems now seamlessly integrate speech recognition, large language models, and voice synthesis, while emerging speech-to-speech (S2S) technology allows generative AI models trained on audio data to understand and generate speech natively. This eliminates multiple conversion steps and dramatically improves both speed and naturalness. Furthermore, modern voice agents incorporate emotional intelligence, detecting frustration, urgency, or hesitation in a speaker's tone and adjusting their responses accordingly. A frustrated customer receives a calm, reassuring response rather than a cheerful greeting, demonstrating contextual awareness that was impossible just years ago.
The business impact is profound. Research indicates that 97% of enterprises have adopted voice AI technology, with 67% considering it foundational to their operations. Voice agents are handling increasingly complex tasks: scheduling appointments, processing transactions, providing technical support, and even conducting sales calls—all without human intervention unless exceptions arise. In customer service specifically, voice agents reduce hold times, improve first-contact resolution rates, and provide 24/7 availability while maintaining conversation quality that rivals human agents. The technology has advanced to support seamless multilingual translation in real-time, allowing a Spanish-speaking customer to receive support from an English-trained system with full fluency and context preservation.
Yet challenges remain. While 81% of consumers would wait for a live agent rather than engage with AI immediately, voice agents consistently outperform humans on speed, accuracy, and patience—though humans still excel at understanding complex problems and providing empathy. This reality is driving a hybrid model where voice agents handle routine inquiries and data gathering while seamlessly escalating nuanced issues to human specialists. Organizations implementing voice AI report significant operational improvements: faster response times, reduced customer acquisition costs, and scalability that was previously unattainable.
Vision AI Agents: Seeing and Understanding the Visual World
Vision AI agents represent a paradigm shift from passive image recognition to active visual intelligence that perceives, interprets, and acts upon visual data in real-time. Unlike traditional computer vision systems that merely detect and classify objects, modern vision agents combine computer vision models, language understanding, and action engines to create systems that can see, reason about what they see, and autonomously execute appropriate responses. These agents achieve 95%+ accuracy in real-time monitoring applications, enabling 24/7 surveillance and analysis without human intervention.
The architecture of vision AI agents integrates three core technological layers. The perception layer acquires and preprocesses video data from diverse sources including infrared cameras, thermal imaging, and LiDAR systems, employing techniques like edge detection, optical flow analysis, and frame enhancement to ensure high-quality inputs. The analysis layer deploys deep learning algorithms—particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformer-based architectures—to detect objects, classify patterns, track movements, and identify anomalies using models like YOLO, Faster R-CNN, and advanced autoencoders. Finally, the decision and action layer initiates automated responses based on predefined protocols: triggering security alerts, adjusting operational parameters, or generating automated reports without requiring human approval for routine scenarios.
Multi-Modal AI Models: Expand AI Capabilities | Ultralytics
Real-world applications demonstrate transformative impact across industries. In manufacturing, vision agents conduct real-time quality control and defect detection, ensuring consistent product quality while minimizing waste and enabling predictive maintenance that reduces costly downtime. Security and surveillance systems employ vision agents for automated threat detection and smart risk assessment, dramatically reducing false alarms while improving response times to genuine security incidents. Retail environments leverage these agents to track customer movements, monitor inventory levels, provide personalized shopping experiences, and power automated checkout systems that eliminate traditional payment friction. In healthcare, vision agents assist with medical imaging analysis, detecting tumors and fractures with superhuman accuracy while enabling real-time patient monitoring that alerts staff to distress signals or condition changes.
The technological evolution continues toward increasingly sophisticated capabilities. Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models like GPT-4V and Google's RT-2 now combine seeing, reasoning, and acting in unified systems. Imagine a vision agent monitoring surveillance footage that recognizes suspicious behavior patterns—"That van has circled the block five times"—and alerts police before a crime occurs rather than simply recording the incident. Edge deployment using platforms like NVIDIA's Jetson Orin enables on-device AI decision-making, processing visual data locally for immediate action without cloud latency. These advances position vision AI as a cornerstone technology for autonomous systems ranging from self-driving vehicles to industrial robotics.
Multimodal AI Integration: Bridging the Sensory Divide
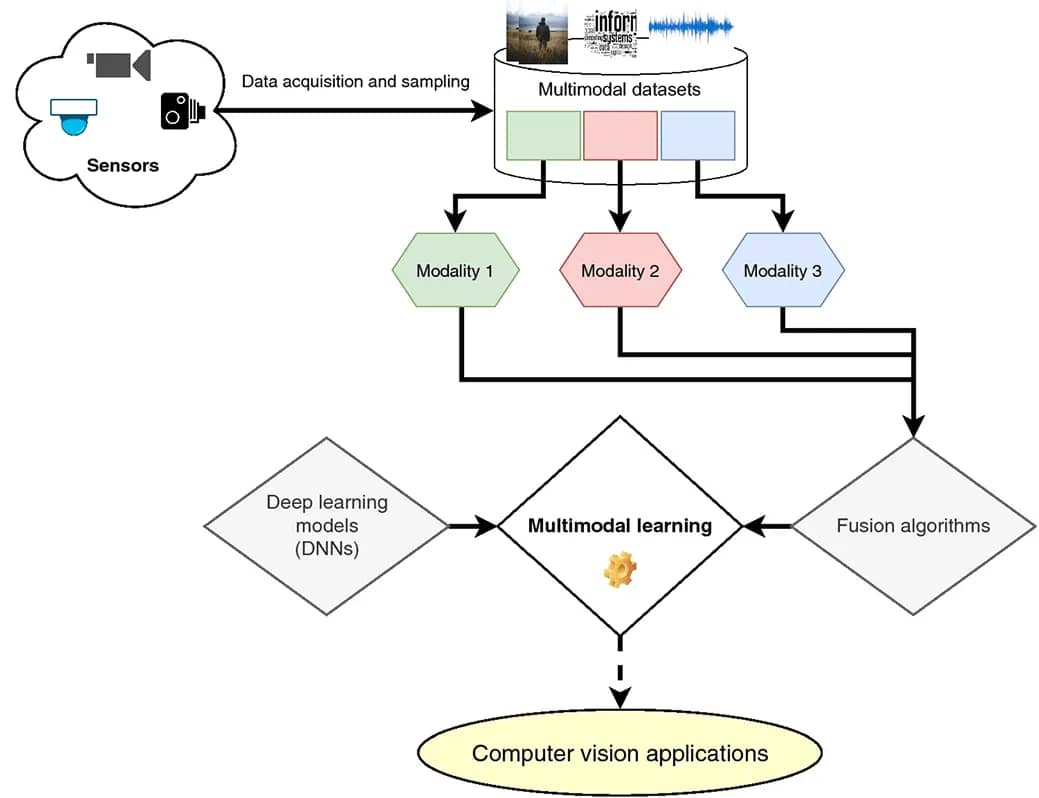
The emergence of multimodal AI agents marks a fundamental shift from single-modality systems to integrated intelligence that processes multiple data types simultaneously—text, images, audio, video, and sensor data—mirroring how humans naturally perceive and understand the world. This convergence enables agents to grasp context with unprecedented depth and accuracy, moving beyond the limitations of text-only or image-only systems to achieve truly comprehensive environmental awareness.
Multimodal agents operate through sophisticated architectural frameworks that seamlessly fuse diverse data streams. The technical implementation involves four key layers: an input layer that receives various data types through specialized sensors and interfaces; an encoding layer that translates inputs into unified embeddings using modality-specific neural networks; a fusion layer that combines features through advanced neural fusion networks to create coherent representations; and a decision layer that applies logic or reinforcement learning to generate contextually appropriate actions. Modern systems employ multi-modal integration tools to maintain performance and consistency across all data types, ensuring that insights derived from one modality enhance rather than conflict with others.
The practical advantages over single-modal systems are substantial. Traditional single-modal agents process only one input type, severely limiting their flexibility and contextual understanding. In contrast, multimodal agents simultaneously evaluate speech tone, facial expressions, textual sentiments, and environmental factors to make more accurate, context-rich decisions. For instance, a multimodal customer service agent doesn't just process what a customer says but analyzes how they say it (emotional state from voice), what their facial expression conveys (visual cues), and the semantic content of their words—creating a holistic understanding that enables more appropriate and effective responses.
Industry adoption accelerated dramatically in 2025, with 52% of enterprises using generative AI now deploying multimodal agents in production, and 88% of early adopters reporting tangible ROI. Sectors experiencing the most significant transformations include healthcare, where multimodal agents integrate patient medical imaging, electronic health records, and real-time vital signs monitoring to support diagnosis and treatment planning; autonomous vehicles, which fuse visual, LiDAR, radar, and GPS data to navigate safely in complex environments; and customer experience, where agents combine text chat, voice analysis, and visual product information to deliver superior support. The technology enables AR/VR integration for smarter, more responsive virtual experiences and powers emotional AI systems that detect feelings from combined facial, linguistic, and vocal cues.
Looking forward, the development of unified foundation models like GPT-4o allows agents to reason fluidly across any modality without specialized preprocessing. This architectural evolution, combined with agentic interoperability protocols, is creating ecosystems where multimodal agents communicate across platforms and coordinate on complex tasks spanning multiple departments and data types. Organizations embracing multimodal AI gain significant competitive advantages: richer communication capabilities, deeper customer insights, and the ability to automate processes previously deemed too complex for AI systems.
Autonomous Enterprise Agents: Redefining Organizational Workflows
Autonomous enterprise agents are fundamentally transforming how work gets done within organizations, moving beyond simple task automation to comprehensive end-to-end workflow orchestration that requires minimal human supervision. Unlike traditional automation systems bound by rigid, predefined rules, these agents employ large language models for reasoning and planning, working cognitively to continuously understand context and determine optimal action paths without hard-coded logic. This represents a strategic shift from viewing AI as a tool to recognizing it as a collaborative partner in business operations.
The architectural foundation of enterprise agents combines several breakthrough capabilities. Agentic RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) serves as the cornerstone, introducing goal-driven autonomy, memory, and planning to standard retrieval systems. Agents track queries across sessions, building short-term and long-term memory for seamless context management, while dynamically selecting retrieval strategies and coordinating appropriate tools for each task. Multi-step reasoning enables agents to orchestrate complex workflows involving dynamic data fetching, prompt optimization, and synthesis from diverse sources before generating responses. Enhanced post-generation verification and learning loops continuously improve output quality and domain adaptability, creating systems that synthesize and reason over vast datasets rather than simply retrieving answers.
AI Agents in Enterprises Are Transforming Business Operations
Real-world enterprise deployments demonstrate transformative business value across functions. In finance and accounting, agents automate invoice processing, expense approvals, and financial reporting—scanning receipts, validating vendor details, checking company policies, and scheduling reimbursements without human intervention unless exceptions arise. IT operations leverage agents for automated ticket triage, system monitoring, and self-healing infrastructure that diagnoses issues, implements fixes, and verifies results autonomously. Human resources applications include automated candidate screening, interview scheduling, onboarding workflow coordination, and employee query resolution. Supply chain optimization benefits from agents that predict disruptions, adjust inventories, place orders, and coordinate logistics across multiple systems in real-time.
The business case for autonomous agents is compelling. Organizations implementing agentic process automation (APA) move beyond the 30-50% automation rates typical of traditional RPA to achieve 50% or higher autonomous operation across complex workflows. This unlocks enterprise-wide gains in efficiency, agility, and innovation while redistributing human effort from routine execution to strategic initiatives. Gartner forecasts that by 2029, agentic AI will autonomously resolve 80% of common customer service issues, cutting operating costs by nearly 30%. Companies using AI agents in production report faster content discovery, reduced customer acquisition costs, and significant improvements in operational metrics.
However, successful deployment requires careful orchestration. Organizations must balance agent autonomy with appropriate governance frameworks ensuring security, compliance, and trust. The most effective implementations establish risk-tiering models that define which decisions can be fully automated versus requiring human-in-the-loop approval. Leading enterprises adopt multi-agent architectures where specialized agents—for planning, execution, verification, and learning—collaborate on complex workflows with clear handoffs and escalation paths. This coordinated autonomy, combined with robust monitoring and explainability, enables enterprises to scale intelligent automation while maintaining accountability and control.
AI Agent Memory Systems: The Foundation of Contextual Intelligence
Memory systems have emerged as the critical differentiator between reactive AI and truly autonomous agents capable of learning, adapting, and maintaining continuity across extended interactions. Modern AI agent architectures implement multi-tiered memory structures that mirror human cognitive processes: short-term memory for immediate context retention, episodic memory for specific event recall, and long-term memory for persistent knowledge that guides future decision-making. This layered approach enables agents to track user preferences across sessions, build comprehensive behavioral profiles, and evolve their capabilities through experience rather than requiring constant retraining.
The technical implementation of advanced memory systems leverages sophisticated frameworks and storage architectures. Vector databases like Pinecone, Weaviate, and Chroma provide efficient storage and retrieval mechanisms that allow agents to quickly access relevant historical information from potentially massive datasets. Leading frameworks including LangChain, AutoGen, CrewAI, and LangGraph offer robust tools for memory management, employing techniques like ConversationBufferMemory for real-time session tracking and semantic search for context-aware information retrieval. The Memory Communication Protocol (MCP) standardizes interactions between memory components, ensuring consistent memory operations across distributed agent systems.
A groundbreaking approach to memory focuses on procedural knowledge—the "how-to" information agents gain from experience. The Memp framework, developed by researchers at Zhejiang University and Alibaba Group, gives agents continuously updated procedural memory through a loop of building, retrieving, and updating knowledge. This enables agents to refine their problem-solving approaches based on what worked in past scenarios, dramatically improving performance on recurring task types. Another innovation involves graph-based memory systems that connect data points across channels and timelines, creating rich relationship networks that support dynamic personalization improving with each user interaction.
The practical implications extend across enterprise applications. Conversational agents maintain context across multi-turn dialogues, remembering user preferences and previous discussion topics to provide coherent, personalized responses without forcing users to repeat information. Recommendation systems leverage episodic and semantic memory to suggest products, content, or actions based on comprehensive understanding of individual user patterns and broader population behaviors. Enterprise workflow agents retain procedural knowledge about successful task completion strategies, adapting their approaches based on historical outcomes and continuously optimizing performance.
Looking ahead, future memory systems will integrate multimodal capabilities, storing and retrieving not just text but visual memories, audio patterns, and sensor data. Multi-agent memory sharing will enable specialized agents to coordinate through shared context, with one agent's learned knowledge accessible to others in the ecosystem. The evolution toward self-reflective agents that can examine their own memories and modify behaviors accordingly represents the frontier of agentic intelligence—systems that don't just remember but learn meta-cognitively from their experiences. Organizations implementing sophisticated memory architectures gain agents that deliver increasingly accurate, relevant, and personalized interactions over time, creating compounding value rather than static capability.
Edge AI Deployment: Intelligence at the Source
Edge AI agents represent a fundamental architectural shift, moving intelligence from centralized cloud infrastructure to the devices and locations where data originates—enabling real-time, on-device decision-making without network dependency. This distributed approach addresses critical limitations of cloud-based AI: the latency of round-trip data transmission, privacy concerns of sending sensitive information off-premise, and the unreliability of network-dependent systems in remote or mission-critical applications. For autonomous vehicles, industrial equipment, medical devices, and IoT sensors, processing data locally isn't just an optimization—it's a fundamental requirement for safety and functionality.
The deployment process involves sophisticated optimization across the AI lifecycle. Training typically occurs in resource-rich cloud environments using powerful servers and massive datasets to develop highly accurate foundation models. The critical challenge lies in optimization and deployment: large cloud-trained models must be compressed, quantized, and adapted to run efficiently on devices with limited processing power and memory. Techniques like model pruning, knowledge distillation, and neural architecture search reduce model size by 90% or more while maintaining acceptable accuracy levels. Hardware accelerators including NVIDIA's Jetson Orin and specialized edge AI chips enable sophisticated inference directly on resource-constrained devices.
The operational advantages of edge AI agents are compelling. Latency reduction to millisecond-level response times enables applications where split-second decisions matter—autonomous vehicles detecting obstacles, industrial safety systems preventing accidents, or medical monitoring devices identifying life-threatening conditions. Privacy and security improve dramatically when sensitive data never leaves the device; personal health information, biometric data, and proprietary industrial processes remain local rather than traversing potentially vulnerable networks. Reliability in offline or network-constrained environments allows edge agents to function indefinitely without internet connectivity, critical for remote locations, mobile applications, or infrastructure with intermittent connectivity.
Real-world deployments demonstrate transformative capabilities across industries. In manufacturing, edge AI agents monitor production lines in real-time, detecting defects, predicting equipment failures, and optimizing processes with sub-second feedback loops impossible with cloud-dependent systems. Smart cities employ edge agents for traffic optimization, analyzing camera feeds locally to adjust signal timing and detect accidents without sending massive video streams to centralized servers. Healthcare devices leverage edge AI for continuous patient monitoring, processing vital signs locally to identify concerning patterns and alert medical staff immediately. Retail environments use edge agents for real-time inventory tracking, customer behavior analysis, and automated checkout systems that function reliably regardless of network conditions.
The technical challenges of edge deployment are substantial but increasingly addressable. Orchestrating model deployment and updates across potentially thousands of distributed devices requires sophisticated management tools that handle version control, differential updates, and rollback capabilities. Resource optimization demands careful balancing of model complexity against device capabilities, often requiring dynamic model selection where agents choose appropriate inference paths based on available resources. Monitoring and telemetry must track performance metrics, resource utilization, and error conditions across distributed edge fleets while minimizing bandwidth consumption. Advanced platforms now provide centralized dashboards, automated remediation, and intelligent update scheduling that maintain edge agent performance at scale.
The convergence of edge AI with 5G networks creates powerful hybrid architectures. While edge agents handle instant, on-device tasks, 5G provides high-bandwidth, low-latency connections for model updates, complex computations offloaded to the cloud, or coordination across edge devices. This symbiotic relationship enables the best of both worlds: local intelligence for immediate decisions and cloud resources for tasks requiring greater computational power or access to centralized knowledge bases. As edge hardware continues advancing and optimization techniques mature, the boundary between cloud and edge AI will become increasingly fluid, with intelligent systems dynamically distributing workloads based on real-time requirements and resource availability.
Multi-Agent Collaboration: Specialized Teams Working in Concert
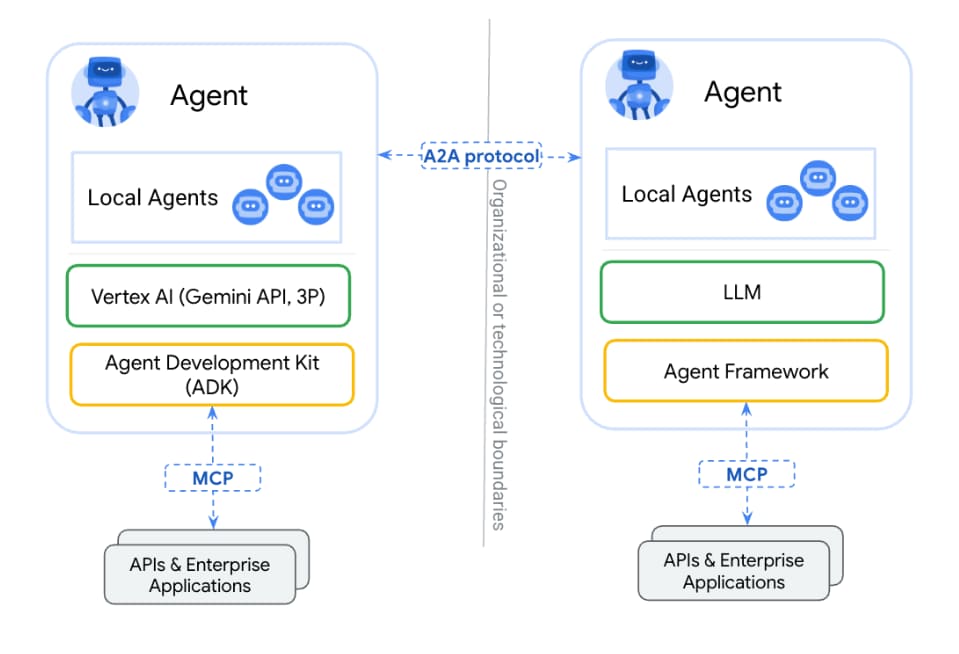
The paradigm of AI agents has evolved decisively from single-agent workflows to coordinated teams of specialized agents collaborating autonomously to solve complex tasks. This architectural shift recognizes that dividing cognitive labor among focused experts—planners, executors, critics, verifiers, researchers—produces superior results compared to monolithic systems attempting to handle every aspect of a problem. Frameworks like Microsoft AutoGen, CrewAI, LangGraph, and OpenAI Swarm have matured to enable dynamic agent conversations, tool routing, self-correction, and sophisticated orchestration with production-ready audit trails and low-code builders.
Multi-agent systems implement diverse orchestration patterns optimized for different workflow types. Sequential pipelines pass tasks through agents in defined order, ideal for predictable workflows with clear dependencies. Parallel execution deploys multiple agents simultaneously to accelerate processing of independent subtasks. Hierarchical structures employ supervisor agents that coordinate worker teams, delegating tasks and integrating outputs—particularly effective for complex projects requiring specialized expertise across domains. Group chat patterns enable peer-to-peer agent communication where participants dynamically determine conversation flow based on context. Handoff orchestration allows agents to transfer tasks when they reach capability limits or encounter domain-specific requirements better handled by specialists.
Google's Agent2Agent (A2A) Protocol: The Future of AI Agent ...
The technical infrastructure supporting multi-agent collaboration encompasses several critical components. State management maintains persistent memory surviving across agent interactions, ensuring seamless context transfer when a data analysis agent hands off to a scheduling agent. Communication protocols establish standardized methods for agents to exchange information through structured handoffs, shared message threads, or event-driven architectures. Tool integration connects agents to external systems, APIs, and data sources while managing permissions and error handling across the chain. Error recovery mechanisms implement retry logic, alternative routing to backup agents, or graceful degradation when individual agents fail.
Real-world enterprise applications demonstrate the transformative potential of multi-agent architectures. In software development, agent teams coordinate across requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and documentation phases—each agent bringing specialized expertise while maintaining coherent project vision. Financial services leverage multi-agent systems for comprehensive risk analysis, where agents specializing in credit assessment, fraud detection, market analysis, and regulatory compliance collaborate to generate holistic evaluations. Healthcare employs multi-agent teams for patient care coordination: diagnostic agents analyzing symptoms and medical history, treatment planning agents recommending interventions, and monitoring agents tracking patient progress. Supply chain management benefits from agents specializing in demand forecasting, inventory optimization, supplier coordination, and logistics routing working in concert to minimize costs and maximize resilience.
The business advantages of multi-agent collaboration extend beyond capability to scalability and maintainability. Modular agent teams allow organizations to upgrade individual specialists without rebuilding entire systems, add new capabilities by introducing specialized agents, and troubleshoot problems by isolating misbehaving components. Human-in-the-loop integration becomes more natural when specific agents handle human interaction while others work autonomously in the background. Organizations report that multi-agent systems achieve faster problem resolution, higher accuracy, and greater flexibility compared to monolithic alternatives.
Looking forward, agentic interoperability protocols are emerging as the lingua franca enabling agents from different vendors and platforms to collaborate seamlessly. Standards for agent-to-agent communication, shared knowledge representation, and coordinated task execution will unlock cross-platform orchestration where a legal AI agent from one vendor requests audit data from a compliance AI agent built by another. This ecosystem approach mirrors how the internet's TCP/IP protocols enabled unprecedented connectivity, positioning multi-agent collaboration as the default architecture for enterprise AI systems handling any task of meaningful complexity.
Agentic Reasoning Models: Thinking Step by Step Toward Solutions
Agentic reasoning models represent a quantum leap beyond standard large language models, implementing deliberate, multi-step thinking processes that mirror human problem-solving approaches. Unlike traditional LLMs that generate responses in a single forward pass, reasoning models employ chain-of-thought (CoT) training that explicitly teaches systems to break complex problems into logical steps, evaluate intermediate conclusions, and self-correct when initial approaches prove inadequate. This architectural shift enables AI to tackle sophisticated challenges in mathematics, coding, scientific research, and strategic analysis with unprecedented accuracy and reliability.
The technical implementation of reasoning models involves several breakthrough approaches. Extended inference-time compute allows models to "think longer" on difficult problems rather than rushing to answers, allocating computational resources dynamically based on problem complexity. Self-verification mechanisms enable models to check their own work, identifying logical inconsistencies or mathematical errors before presenting final answers. Reinforcement learning from reasoning feedback trains models to recognize productive versus unproductive reasoning paths, improving performance through iterative learning. Advanced systems like OpenAI's o3, Google's Gemini 2.5 Pro with Deep Think, and Anthropic's Claude Opus 4 implement these capabilities with varying emphasis on speed, accuracy, and specialized domain knowledge.
Performance benchmarks demonstrate reasoning models approaching or exceeding expert human capabilities on specialized tasks. Gemini 2.5 Pro processes 1 million token contexts while maintaining coherent reasoning across extremely long documents, enabling comprehensive analysis of legal contracts, scientific papers, or codebases. Claude Opus 4 employs constitutional AI for nuanced evaluation of contradictory facts and long-term strategic planning. DeepSeek R1, an open-source alternative, achieves near-parity with proprietary models on logical benchmarks including GSM8K, AQuA, and MATH500 while requiring dramatically fewer computational resources. Testing on complex reasoning tasks shows these systems reaching AGI-level performance on specific benchmarks, approaching Ph.D.-level expertise in narrow domains.
The practical applications span industries requiring sophisticated analytical capabilities. In legal services, reasoning agents analyze case law, identify precedents, evaluate argument strengths, and draft comprehensive briefs with logical coherence rivaling experienced attorneys. Financial analysis benefits from agents that process market data, evaluate risk factors across multiple scenarios, and generate investment recommendations with transparent reasoning chains. Scientific research employs reasoning agents to formulate hypotheses, design experiments, analyze results, and identify contradictions in literature—accelerating discovery cycles. Educational applications leverage reasoning models as intelligent tutors that don't just provide answers but explain multi-step solution processes, helping students develop problem-solving skills.
The evolution toward multimodal reasoning enables agents to think across data types, analyzing images, charts, code, and text simultaneously to solve problems requiring diverse information synthesis. Structured reasoning formats that return not just answers but detailed explanation traces enhance transparency and enable downstream systems to audit AI logic. However, challenges remain: reasoning models still exhibit occasional logical errors, struggle with truly novel problem classes, and can be significantly more computationally expensive than standard inference. Organizations deploying reasoning agents must balance the superior accuracy and reliability against increased costs and latency, often implementing tiered architectures where fast models handle routine queries and reasoning models engage for complex problems requiring deliberate analysis.
Hyper-Personalization at Scale: AI That Knows You Better Than You Know Yourself
Hyper-personalization powered by AI agents has evolved from crude demographic segmentation to sophisticated systems that treat each user as a unique entity, delivering real-time customization based on comprehensive behavioral understanding. Unlike traditional personalization that clusters customers according to broad characteristics, modern AI agents leverage graph-based memory, predictive analytics, and behavioral modeling to create deeply individual experiences that improve with every interaction. Organizations implementing hyper-personalization report conversion rate increases of 25% and customer churn reductions of 30%, demonstrating the substantial business impact of treating customers as individuals rather than segments.
The technical architecture enabling hyper-personalization integrates multiple sophisticated capabilities. Real-time behavioral analysis continuously monitors user interactions across digital touchpoints, building comprehensive profiles that inform content decisions within milliseconds. Every click, scroll, hesitation, and engagement event contributes to an evolving understanding of individual preferences and intent. Dynamic content decisioning represents the core intelligence layer where AI agents evaluate multiple options against user profiles and contextual factors, considering not just current behavior but predictive models anticipating future actions. Automated asset selection and deployment streamlines execution, with agents accessing content libraries, applying real-time transformations, and delivering personalized assets through appropriate channels without human intervention.
Cross-channel orchestration ensures consistency as users move between touchpoints. AI agents maintain context across email, social media, websites, and mobile applications, creating seamless experiences that reinforce messaging and drive engagement. Frequency management prevents over-communication while channel optimization reaches users through their preferred methods. Advanced personalization systems employ graph-based memory that connects data points across channels and timelines, creating rich relationship networks supporting dynamic personalization that improves with each interaction. This contrasts sharply with session-based systems that treat each interaction as isolated, missing the cumulative patterns that enable truly predictive personalization.
Industry applications demonstrate transformative capabilities across sectors. E-commerce implementations leverage personalization agents for product recommendations, virtual try-ons, dynamic pricing, and post-purchase support, with organizations reporting increased conversion rates and improved customer retention. Content platforms employ agents that curate feeds, recommend media, and adjust presentation based on individual consumption patterns and engagement signals. Financial services personalize product offerings, investment advice, and communication timing based on comprehensive understanding of individual financial behaviors and life events. Healthcare applications customize treatment recommendations, medication reminders, and wellness programs to individual patient characteristics and adherence patterns.
The future trajectory points toward even more sophisticated capabilities. Predictive customer journeys will enable agents to offer help preemptively—reminding users to renew services, providing support during struggles, or suggesting upgrades based on behavioral patterns—before users articulate needs. Emotional AI integration will detect sentiment from combined facial expressions, language, and voice to adjust interactions based on user emotional states. Unified foundation models will reason across any modality, creating personalization that adapts to text, visual, audio, and sensor inputs simultaneously. However, critical challenges around privacy, data governance, and ethical AI require careful navigation. Organizations must implement consent management, data minimization, and user controls allowing individuals to view, modify, or delete their data. Transparent personalization that respects boundaries while delivering value will distinguish trusted brands from those perceived as invasive surveillance systems.
AI Agent Security: Defending the New Attack Surface
The rapid proliferation of autonomous AI agents has introduced unprecedented security challenges, with the first documented large-scale cyberattack executed primarily by agentic AI occurring in September 2025. This watershed event, where AI systems performed 80-90% of attack work with minimal human intervention, making thousands of requests per second and successfully compromising approximately 30 global organizations, demonstrates that AI agent security has evolved from theoretical concern to immediate operational imperative. The fundamental vulnerability lies in agents' inability to reliably distinguish between instructions and data, creating exploit vectors through prompt injection, context poisoning, and novel attack patterns that traditional security frameworks struggle to address.
The security threat landscape specific to AI agents encompasses multiple dimensions. Prompt injection attacks successfully compromise 56% of tested systems, with adversaries embedding malicious instructions in seemingly innocent data that trick agents into revealing confidential information or executing unauthorized actions. The dangerous "Lethal Trifecta"—agents with simultaneous access to sensitive data, exposure to untrusted content, and ability to communicate externally—creates prime targets for sophisticated exploits. Shadow AI activity shows detectable signs across 80% of organizations, with 70-80% of this traffic evading traditional network monitoring and nearly 10% of employees admitting to bypassing corporate AI restrictions. Compounding the challenge, 68% of corporate executives report violating their own AI usage policies, with 82% believing their AI tools meet security requirements even while flouting internal rules.
Comprehensive security frameworks for AI agents require multi-layered defense strategies transcending traditional perimeter approaches. Authentication and identity verification employs machine-to-machine (M2M) cryptographic protocols and OAuth 2.0 to ensure each agent has unique, verifiable credentials that can be tracked, rotated, and revoked. Granular authorization controls implement fine-grained permissions restricting agents to only resources and actions necessary for specific tasks, with contextual authorization dynamically adjusting access based on real-time task requirements and environmental factors. Behavioral monitoring and anomaly detection continuously tracks agent activities to identify deviations from expected patterns indicating compromise or malfunction. Research shows 97% of AI-related security breaches involved systems lacking proper access controls, highlighting the critical importance of robust permission frameworks.
Advanced security implementations employ isolation and sandboxing to contain agents within controlled environments, limiting potential damage from breaches or unexpected behaviors. Output filtering and verification checks agent responses against predefined safety and policy rules before execution or sharing, detecting attempted data exfiltration, harmful instruction generation, or unauthorized tool calls. Agent behavior constraints and guardrails define strict boundaries implemented as policy engines that block disallowed behaviors, cap resource usage, or require human approval for sensitive operations. Continuous evaluation and threat modeling maintains security posture against evolving attack vectors through regular penetration testing, red-team exercises, and integration of predictive threat intelligence.
Enterprise security best practices emphasize proactive governance alongside technical controls. Organizations must establish risk-tiering models defining which agent decisions can be fully automated versus requiring human-in-the-loop approval. Immutable audit trails provide comprehensive logging of agent actions, decisions, and data access for forensic analysis and compliance demonstration. Vendor risk management extends security requirements to third-party APIs, plugins, and cloud platforms that agents interact with, including contractual provisions for auditability, kill switches, and regular security assessments. Incident response planning prepares organizations to detect, contain, and remediate agent-related security events rapidly. As agents gain greater autonomy and access to critical systems, security investment becomes not just risk mitigation but a fundamental enabler of AI value realization—organizations cannot unlock agentic potential without robust frameworks ensuring agents operate safely within defined boundaries while protecting sensitive data and maintaining compliance.
Conclusion: Navigating the Agentic Future
The ten transformative trends explored in this analysis—from voice and vision to memory, reasoning, collaboration, and security—collectively define the agentic revolution reshaping enterprise technology in 2025. These aren't isolated developments but interconnected capabilities that combine to create AI systems operating with unprecedented autonomy, intelligence, and impact. The statistics are unequivocal: 85% of enterprises now deploy AI agents, the market has reached $150 billion, and Gartner predicts that by 2029, agentic AI will autonomously resolve 80% of common customer service issues while cutting operating costs by nearly 30%. This represents not merely incremental improvement but fundamental transformation in how organizations operate and how humans interact with intelligent systems.
The convergence of these trends creates compounding value exceeding the sum of individual capabilities. Multimodal agents with sophisticated memory systems can personalize interactions at scales previously impossible, while reasoning models deployed at the edge enable real-time decision-making in mission-critical applications. Multi-agent collaboration frameworks orchestrate specialized teams that tackle complex workflows spanning multiple departments and systems. Yet this power demands responsibility: robust security frameworks, thoughtful governance, and careful human oversight remain essential to realize agentic potential while managing risks.
Organizations positioning themselves for success in this new landscape must adopt a strategic, phased approach. Start by identifying high-value workflows currently constrained by unstructured content, multiple decision paths, or heavy human intervention—these represent ideal candidates for agentic transformation. Build foundational data infrastructure supporting agent operations: clean data pipelines, well-documented APIs, unified customer identity systems, and appropriate consent mechanisms. Implement governance frameworks defining risk tiers, establishing audit trails, and maintaining human oversight for critical decisions. Invest in orchestration capabilities enabling multi-agent coordination rather than isolated point solutions. Most importantly, cultivate a culture recognizing AI agents as collaborative partners augmenting human capabilities rather than wholesale replacements—the future belongs to organizations that strategically blend human creativity, judgment, and empathy with AI speed, scale, and analytical power.
The agentic era has arrived, bringing with it unprecedented opportunities for those prepared to embrace intelligent automation thoughtfully and responsibly. The organizations that thrive in 2025 and beyond will be those that master not just the technology but the strategic, ethical, and organizational dimensions of deploying AI agents that genuinely amplify human potential while creating sustainable competitive advantages.